Delving into the fascinating world of evolution, the evolution natural and artificial selection gizmo provides a captivating platform to explore the intricate mechanisms that shape the diversity of life. This comprehensive exploration unveils the profound influence of natural selection in driving the adaptation of species to their environments, while simultaneously examining the transformative power of artificial selection in shaping the characteristics of domesticated organisms.
Throughout this inquiry, we will embark on a journey that unravels the intricate tapestry of evolutionary processes, uncovering the factors that influence the rate and direction of change, while delving into the ethical implications and potential applications of manipulating the course of evolution.
Through the lens of the Gizmo simulation, we will gain a deeper understanding of the interplay between natural and artificial selection, illuminating their profound impact on the evolution of species.
Natural Selection
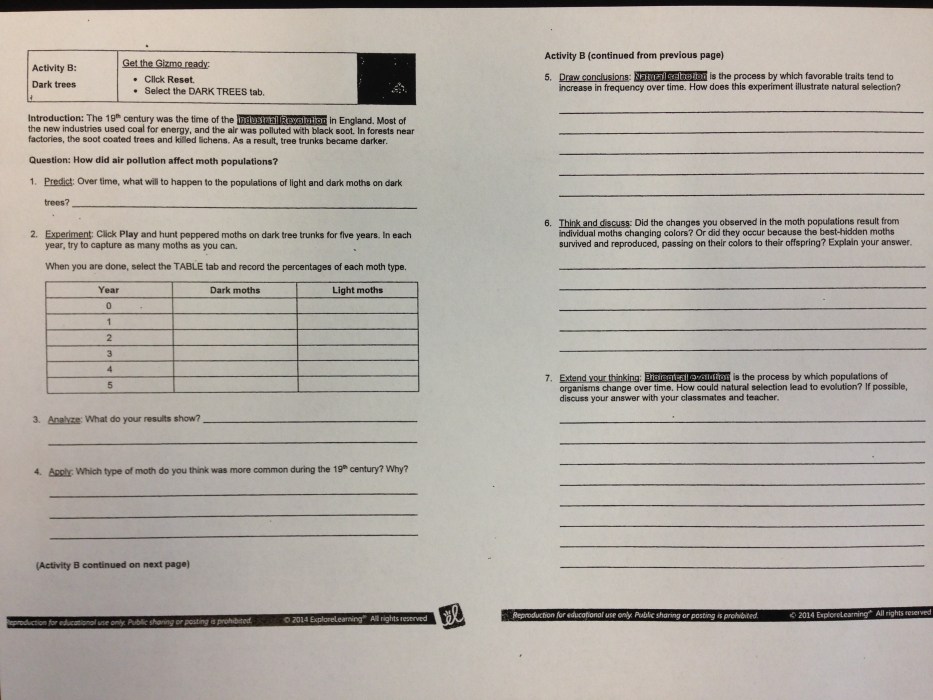
Natural selection is a fundamental mechanism driving evolution. It is a process by which heritable traits that increase an organism’s survival and reproductive success become more common in a population over generations. These advantageous traits are passed down from parents to offspring, gradually leading to changes in the genetic makeup and physical characteristics of a species.
Examples of Natural Selection in Action
- In the peppered moth, darker moths were better camouflaged against soot-covered trees during the Industrial Revolution, resulting in a shift towards darker moths in polluted areas.
- Antibiotic resistance in bacteria: Bacteria with genes conferring resistance to antibiotics survive and reproduce more successfully in the presence of antibiotics, leading to a gradual increase in antibiotic resistance in bacterial populations.
Factors Influencing the Rate of Natural Selection
- Strength of selection pressure: The more advantageous a trait is, the stronger the selection pressure and the faster the rate of natural selection.
- Heritability: The degree to which a trait is genetically determined influences the rate of natural selection.
- Population size: Larger populations experience slower rates of natural selection due to the greater genetic diversity.
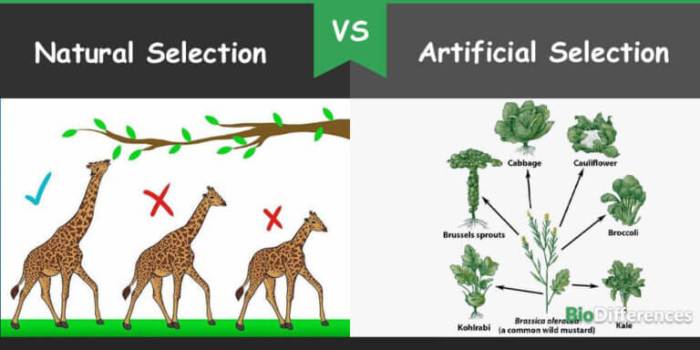
Artificial Selection

Artificial selection, also known as selective breeding, is a process by which humans intentionally breed organisms with desired traits. Unlike natural selection, which is driven by environmental pressures, artificial selection is guided by human preferences.
Examples of Artificial Selection in Practice
- Domestication of animals: Humans have bred animals for specific traits such as increased milk production in cows, faster growth in chickens, and desired coat colors in dogs.
- Development of crop varieties: Farmers select and breed plants with desirable traits such as increased yield, disease resistance, and improved nutritional value.
Ethical Implications of Artificial Selection
Artificial selection raises ethical concerns regarding the potential manipulation and exploitation of organisms. Ethical considerations include:
- Animal welfare: Ensuring the well-being and humane treatment of animals used in artificial selection practices.
- Genetic diversity: Maintaining genetic diversity to prevent inbreeding and potential loss of beneficial traits.
- Unintended consequences: Assessing the potential long-term effects of artificial selection on ecosystems and biodiversity.
Gizmo Simulation: Evolution Natural And Artificial Selection Gizmo

The Gizmo simulation provides a virtual environment to explore the principles of natural and artificial selection. It allows users to manipulate factors such as environmental conditions, genetic variation, and population size to observe the effects on the evolution of a simulated population.
How the Simulation Demonstrates Natural Selection, Evolution natural and artificial selection gizmo
The simulation models a population of organisms in a changing environment. Individuals with traits that increase their survival and reproduction have a higher chance of passing on their genes, leading to a gradual shift in the population’s genetic makeup.
How the Simulation Demonstrates Artificial Selection
In the artificial selection mode, users can select specific traits to breed for. The simulation shows how human intervention can rapidly alter the genetic makeup of a population, leading to the development of desired characteristics.
Limitations of the Simulation
While the simulation provides a simplified representation of natural and artificial selection, it has limitations:
- It does not account for the complexity of real-world ecosystems and genetic interactions.
- It assumes a relatively short timeframe, which may not accurately reflect the slow pace of evolution in nature.
Comparison of Natural and Artificial Selection
| Factor | Natural Selection | Artificial Selection |
|---|---|---|
| Source of Variation | Genetic variation within a population | Human-selected traits |
| Role of the Environment | Drives selection pressures based on survival and reproduction | Influenced by human preferences and goals |
| Timescale of Change | Gradual, over many generations | Relatively rapid, within a few generations |
Implications for the Evolution of Species
The differences between natural and artificial selection have significant implications for the evolution of species:
- Natural selection drives the adaptation of species to their environments, while artificial selection focuses on human-desired traits.
- Natural selection promotes genetic diversity, while artificial selection can lead to reduced genetic diversity due to selective breeding for specific traits.
- Artificial selection can accelerate the rate of evolution, but it also carries the potential for unintended consequences, such as the loss of beneficial traits or the emergence of genetic disorders.
Applications of Evolution
The principles of evolution have wide-ranging applications in various fields:
Medicine
- Development of antibiotics and vaccines based on an understanding of how bacteria and viruses evolve.
- Personalized medicine: Tailoring treatments to individual patients based on their genetic makeup.
Agriculture
- Breeding crops and livestock with improved yield, disease resistance, and nutritional value.
- Conservation: Managing ecosystems and protecting endangered species by understanding the evolutionary processes that shape them.
Potential Future Applications
Evolutionary science holds promise for future applications, including:
- Synthetic biology: Designing and engineering organisms with desired traits.
- Predicting the evolution of infectious diseases to develop more effective prevention and treatment strategies.
- Understanding the long-term effects of climate change on species and ecosystems.
FAQ Explained
What is the primary distinction between natural and artificial selection?
Natural selection is driven by environmental pressures, favoring individuals with traits that enhance their survival and reproductive success. In contrast, artificial selection is directed by human intervention, selectively breeding organisms for desired characteristics.
How does the Gizmo simulation contribute to our understanding of evolution?
The Gizmo simulation provides an interactive platform to visualize and experiment with the principles of natural and artificial selection. It allows users to manipulate environmental conditions and breeding strategies, gaining insights into the dynamics of evolutionary processes.
What are the ethical implications of artificial selection?
Artificial selection raises ethical concerns regarding the potential consequences of manipulating the genetic makeup of organisms. Considerations include the well-being of individuals, the impact on genetic diversity, and the potential unintended effects on ecosystems.